Search Results for: active site
Active site
Definition noun, plural: active sites The specific region of an enzyme where a substrate binds and catalysis takes place or... Read More
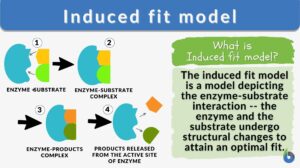
Induced fit model
Induced-Fit Model Definition The induced-fit model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction to depict the dynamic... Read More
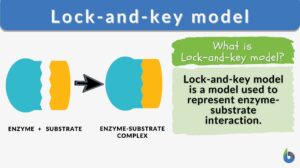
Lock-and-key model
Lock-and-key model Definition Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
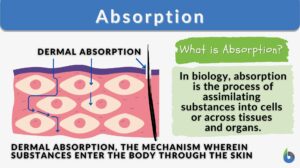
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More
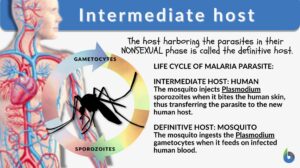
Intermediate host
Intermediate Host Definition When looking at the relationships amongst different biological members of our biosphere, we... Read More
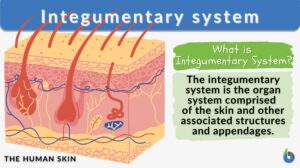
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Zymogen granules
Definition noun The granules in the cytoplasm of secretory cells containing the zymogen Supplement Zymogen granules are... Read More
Reverse passive agglutination
Definition noun A type of agglutination reaction in which known antibody is bound to a carrier particle instead of the... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
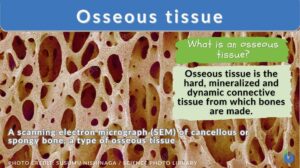
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Gap 2-M DNA damage checkpoint
Definition noun (cell biology) A control mechanism in G2 phase of the cell cycle that ensures the cell is ready for cell... Read More
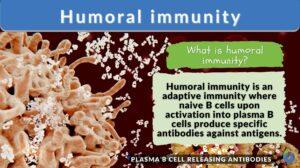
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
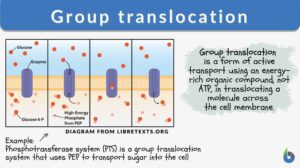
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Plant Meristems and Growth
A common mistake that many people assume is that an increase in size means an increase in growth. This is not the case.... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More